
Presentation of Théo Nicolazo’s first research résults
Presentation of Théo Nicolazo’s first research résults
Théo Nicolazo presented the first results from his Research and Innovation project at ESA, L’Ecole supérieure des agricultures during the annual congress of the EAAP – European Federation of Animal Science in Porto.
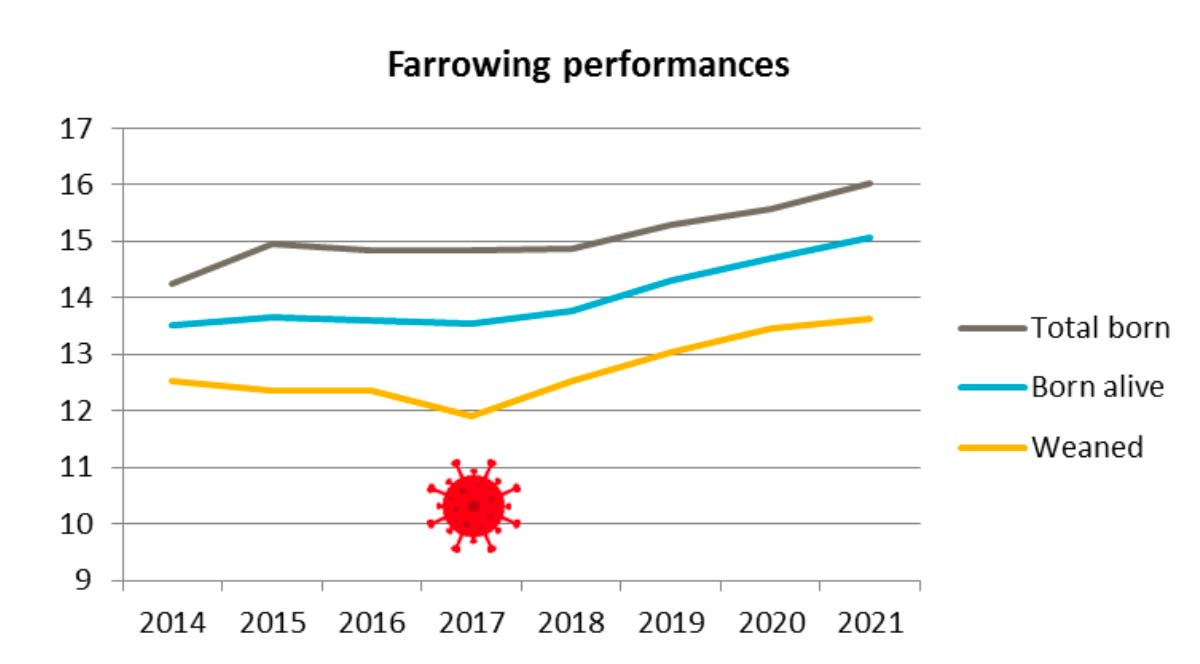
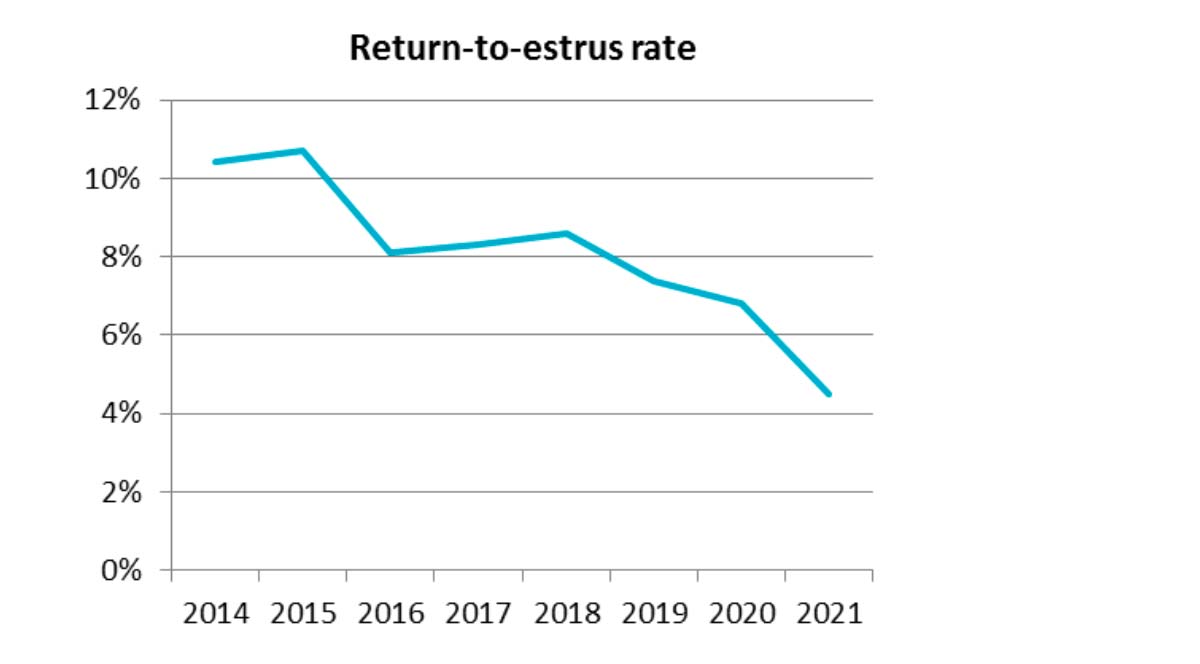
Congratulations Théo Nicolazo for your oral communications during the annual congress of EAAP – European Federation of Animal Science 2022 ! The main objectives of this project was to give some scientific proofs about the consequences of stray voltages in pig housing on behaviour and physiological stress. All the team thank Elodie Merlot, Caroline Clouard, Raphaël Comte and Sophie Dare of the PEGASE group of INRAE for their advices in designing the protocol and analysing the data.









Recent Comments